File : D1.4
Author : Joanna I. House (UNIVBRIS) et al.
Transparency, accuracy, completeness, comparability, and consistency of national Greenhouse gas inventories in ensured through Quality Assurance and Quality Control (internal checks and reviews) and Verification (review using independent data and methods). The inventory reports and the progress of mitigation actions under NDC and the support provided by developed countries are subject to a technical expert review to check with the modalities, procedures and guidelines of the enhanced transparency framework. Under the Global Stocktake (every five years starting from 2023) the countries’ collective progress is assessed towards the long term goals of the PA based on the best available science. Data for independent review includes that compiled by other data providers e.g. FAO, EDGAR,
USEPA. In the land sector, satellite and other airborne senor data (e.g. radar, Lidar) can provide estimates of land cover change and biomass which can be sued for developing or verifying inventories. Atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gasses from satellites and tall towers can also be sued with inverse modelling techniques to derive greenhouse gas flux, however this works best for fossil fuels and other industrial sources, especially when isotopes and other tracer gasses are used. These techniques are already in use with the UK and Swiss inventory. For the land sector it is not possible to separate emissions and removals due to natural and anthropogenic causes, although site specific measurements and other trace gasses can be used to indicate some sources as has been done to support the methane inventory BUR in India.
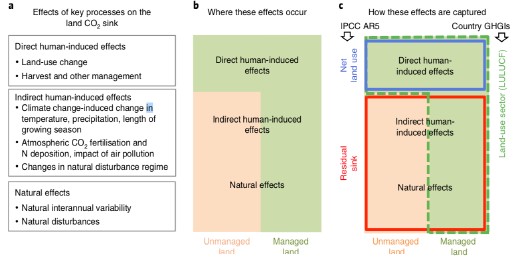
Figure 1 : The effects of key processes (a) and where they occur (b) as well as how these effects are captured in the science-based approaches compared to the National GHGIs.
